

Their main advantage is the reliable repeatability of the measurements – unlike the manual dew scope described below, the measurements a completely objective and automatic. These analyzers use a chilled mirror sensor to determine the hydrocarbon dew-point temperature of the gas sample accurately and automatically. Online optical hydrocarbon dew-point analyzers There are a number of different accepted methods for measuring hydrocarbon dew point which have been developed over time. Therefore, an accurate determination of the HCDP requires evaluation of distribution of the individual components in the C6+ fraction (at least C9 but possibly higher). The presence of heavier hydrocarbons will increase the HCDP and failure to include them in a HCDP calculation will under-predict the HCDP. The HCDP is very sensitive to the specific components of the gas stream and is strongly influenced by the concentration of the heavier hydrocarbons, especially C6+. Gas composition, contaminants and additives, high pressures, and the presence of corrosive compounds vary from pipeline to pipeline and all affect the results of measurements. Hydrocarbon Dew Point (HCDP) is not an easy parameter to measure. Typical Phase Envelope for 3 Stages of Natural Gas Difficulties in measuring hydrocarbon dew point The chilled gas temperature becomes the new HCDP of the gas stream. As the gas is cooled below its original dew point temperature, the entire dew point curve shifts cooler for the remaining gas phase that is now depleted in heavier components. When condensate forms from a gas mixture, the distribution of hydrocarbons changes so that the liquid phase becomes enriched in the heavier components while the gas phase becomes depleted of these heavier components.

Note that given the shape of the phase envelope, the measurement of hydrocarbon dew point and potential hydrocarbon liquid is usually carried out at a pressure between 25 and 30 bar (ideally 27 bar) where liquid drop out occurs at the highest temperatures. The maximum pressure at which liquids can form is called the cricondenbar, and the maximum temperature at which liquids can form is called the cricondentherm. The word “retrograde” means moving backward and this phenomenon was given the name because it is contradictory to the phase behavior of pure components, which condense with increasing pressure and/or decreasing temperature. This phase envelope phenomenon provides for behavior known as retrograde condensation. Typical Water and Hydrocarbon Phase Envelopes for Transmission Quality Natural Ga Two dew point temperatures are possible at a given pressure and two dew point pressures are possible at a given temperature. The dew point line divides the two-phase gas-liquid region and the single-phase gas region. It is typically displayed on a phase diagram (see below) as a function of gas pressure and temperature, for natural gas with a given composition.
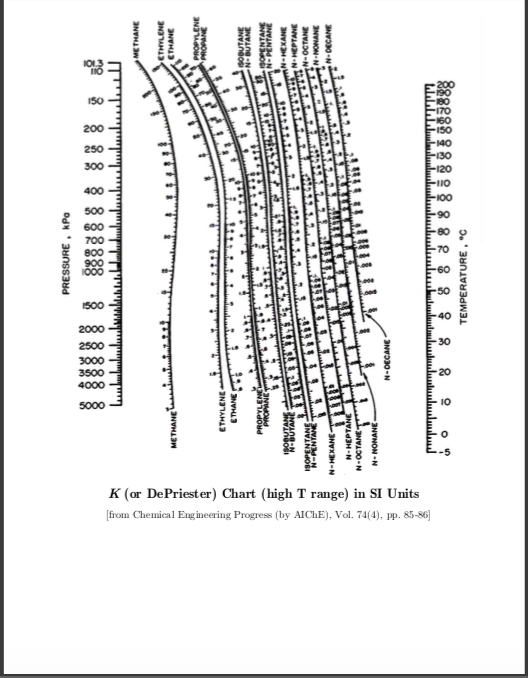
Depriester chart dew point series#
The HCDP is defined as the series of matching pressure and temperature points at which hydrocarbons condense into liquid from a natural gas mixture. This is an important parameter for pipeline operators: if the natural gas contains a high proportion of heavy hydrocarbons there is a greater risk of liquid condensate forming in the pipeline. Therefore, a higher HCDP normally indicates a higher proportion of heavy hydrocarbon components. It’s sometimes referred to as “hydrocarbon liquid drop-out”. Hydrocarbon dew point (HCDP) indicates the temperature at which heavy hydrocarbon components begin to condense out of the gaseous phase when the gas is cooled at constant pressure. How is hydrocarbon dew point defined by the industry? So the term ‘natural gas’ describes a gas mixture that contains a wide range of hydrocarbons, from light short chain aliphatics (non-aromatic compounds) to heavy, long chain molecules. The result is a gas mixture with a high proportion of methane, but which still contains varying amounts of ethane, propane, and butane. Further processing removes CO2 and H2S before reduced temperature separation extracts entrained condensates and reduces the concentration of non-methane hydrocarbons such as the natural gas liquids (NGLs) – ethane, propane, butane, iso-butane and natural gasoline. Initial processing dries the gas to remove liquid water and reduce water vapor concentration. As well as methane, other hydrocarbon constituents include ethane (C2H6), propane (C3H8), and butane (C4H10).

Undesirable non-hydrocarbon constituents include carbon dioxide, hydrogen sulfide and moisture. Methane is the major component, typically between 60 to 90%, with other components present in different proportions, from high percentages to traces at less than 0.01%. At the point of extraction, natural gas comprises 20 or more individual hydrocarbon and non-hydrocarbon constituents.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
